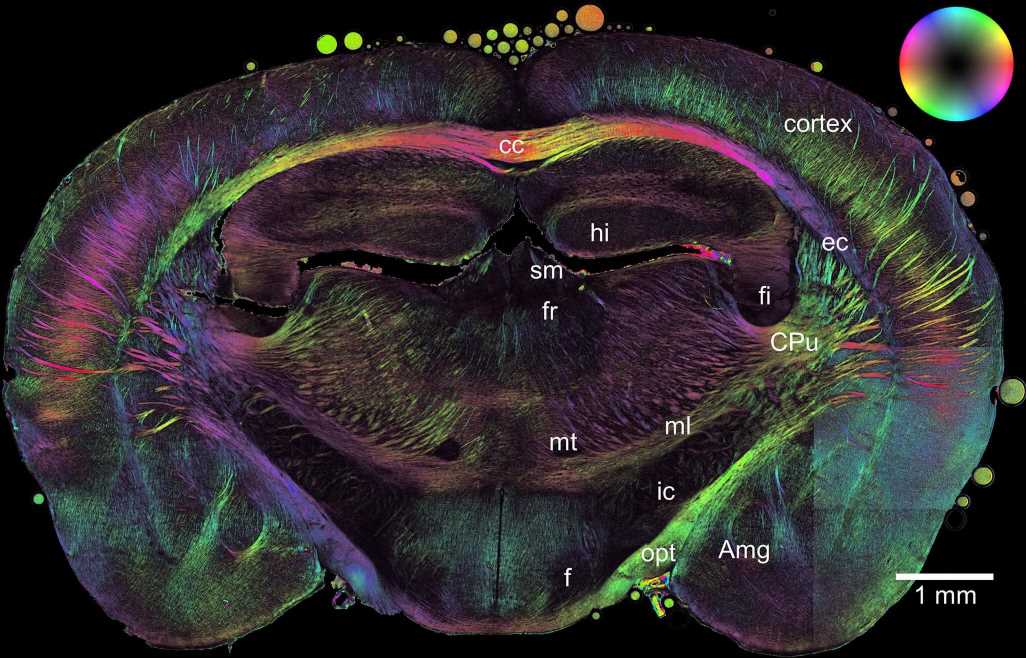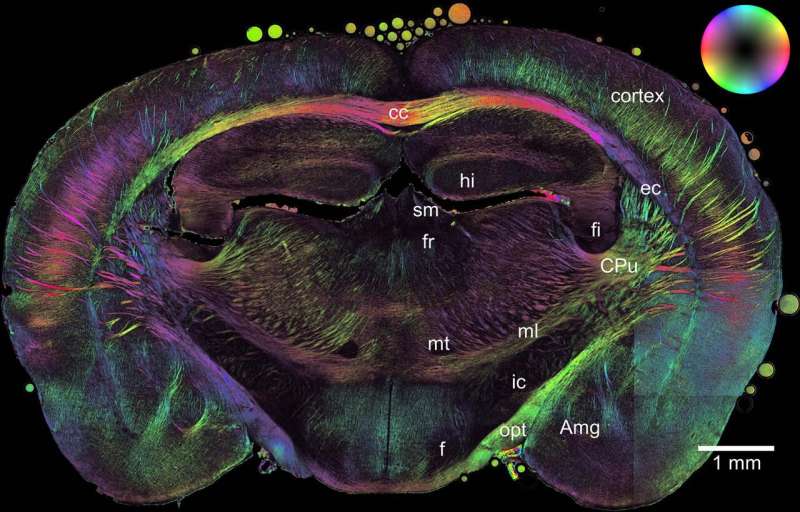
The brain can be divided into so-called gray matter and white matter. The white matter contains the axons that transmit stimuli. For faster stimulus transmission, the axons are wrapped in an insulating layer of myelin, in the same way as a cable is wrapped in rubber insulation to ensure that no electricity is lost along the way.
If the myelin sheath is damaged or degraded, this leads to impaired brain and body functions. In multiple sclerosis, for example, the insulating myelin layer is severely impaired. However, the exact causes of the disease are still unclear.
Researchers at the Jülich Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine and the Jülich Centre for Neutron Science have developed a new imaging method at the small-angle scattering facility KWS-1 at the MLZ to map the density, structure, and spatial orientation of nerve fibers and myelin.
New method complements previous procedures
“For a long time now, it has been possible to determine the spatial orientation of nerve fibers in brain slices using light microscopy and polarization,” explains Dr. Heinrich Frielinghaus from the JCNS, head of the KWS-1 group, “but the exact structure and orientation of the myelin on the molecular scale cannot be detected using light.” With the help of neutrons, the researchers can now for the first time determine both structure and orientation, and correlate these with polarization measurements.
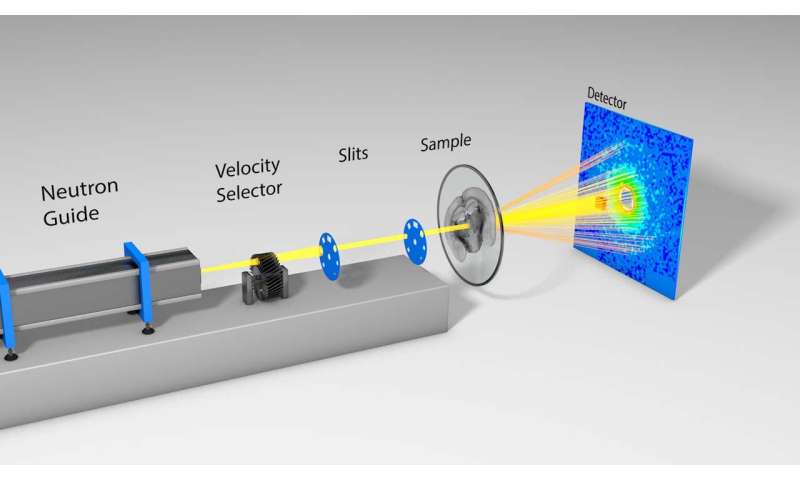
The special feature of this new method is that it allows scientists to image the axons bundled into nerve fibers at the same time as the insulating myelin sheath.
“With our neutron-based method, we can confirm the results of previous methods and provide additional information,” says Frielinghaus.
Applications in medicine
“Since we work with brain slices, it is of course not a diagnostic procedure,” explains Frielinghaus. With their new method, the researchers hope to better understand the causes of neurological diseases in the future by being able to visualize structural changes in the brain more completely.
Source: Read Full Article