In the field of optogenetics, scientists investigate the activity of neurons in the brain using light. A team led by Prof. Dr. Ilka Diester and Dr. David Eriksson from the Optophysiology Laboratory at the University of Freiburg has developed a new method to simultaneously conduct laminar recordings, multifiber stimulations, 3D optogenetic stimulation, connectivity inference, and behavioral quantification on brains. Their results are presented in Nature Communications. “Our work paves the way for large-scale photo-recording and controlled interrogation of fast neural communication in any combination of brain areas,” Diester explains. “This can help us unravel the rapid and multilayered dialogs between neurons that maintain brain function.”
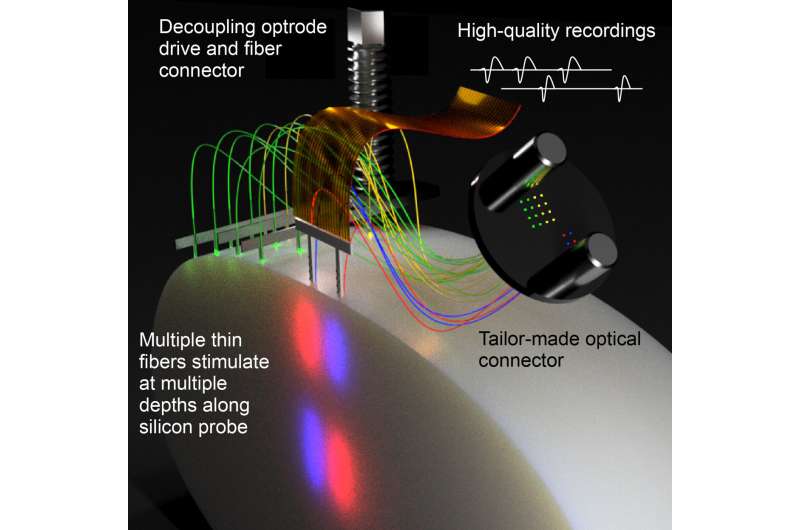
The research group, in collaboration with Dr. Patrick Ruther of the Department of Microsystems Engineering (IMTEK) at the University of Freiburg, is developing a new method for the controlled interrogation and recording of neuronal activity in the brain. To do this, the team is taking advantage of thin, cell-sized optical fibers for minimally invasive optogenetic implantation. “We combine side-emitting fibers with silicon probes to achieve high-quality recordings and ultrafast, multichannel optogenetic control.”
They call the system Fused Fiber Light Emission and eXtracellular Recording, or FFLEXR. In addition to optical fibers that can be attached to any silicon probe, the team uses linear depth-resolved stimulation, a lightweight fiber matrix connector, a flexible multifiber ribbon cable, an optical commutator for efficient multichannel stimulation, a general-purpose patch cable, and an algorithm to manage the photovoltaic response.
“Our alternative approach maintains the flexibility to apply any desired wavelength via an external interchangeable light source and enable optogenetic stimulation at different depths of brain tissue,” Diester says.
Source: Read Full Article
