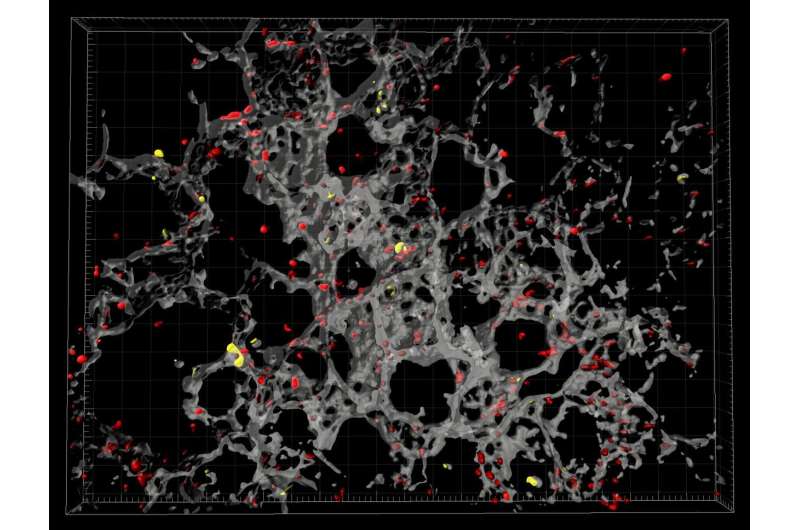
Treating patients with acute respiratory failure is a constant challenge in intensive care medicine. In most cases, the underlying cause is lung inflammation triggered by a bacterial infection or—more rarely, despite being frequently observed at present due to the corona pandemic—a viral infection. During the inflammation, cells of the immune system—the white blood cells—migrate to the lungs and fight the pathogens. At the same time, however, they also cause ‘collateral damage’ in the lung tissue. If the inflammatory reaction is not resolved in time, this can result in chronic inflammation with permanent impairment of lung function. Together with colleagues from London, Madrid and Munich, a research team at the University of Münster headed by Prof Jan Rossaint and Prof Alexander Zarbock, two specialists in anaesthesiology and intensive care medicine, has gained new insight into the cellular processes involved in bacterial lung inflammation. In a study on mice, the researchers found that the interaction between platelets and certain white blood cells—the regulatory T cells—play a significant role in resolving the inflammation. The study has been published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Platelets partner with regulatory T cells and send signals to scavenger cells
It was already known that, at the beginning of an inflammatory reaction in the lungs, as is the case with other organs, platelets work together with neutrophil granulocytes—a subgroup of white blood cells that specialize in fighting off pathogens. However, for the first time, the team of scientists has now shown that, as the inflammation progresses, platelets bind to regulatory T cells and that this binding is needed for the migration of the T cells, together with the platelets, to the site of inflammation in the lungs. Upon their arrival, they work together secreting anti-inflammatory messenger substances which “reprogramme” the macrophages in the lungs. These white blood cells, also known as scavenger cells, then stop directing neutrophil granulocytes to the site of inflammation, instead eliminating the neutrophil granulocytes that are no longer needed. This helps the inflammation subside and prevents further tissue damage.
Search for new therapy concepts
Source: Read Full Article
